The Main Factors That Cause the Air in Earths Atmosphere to Move. Air from higher in the atmosphere sinks down to fill the space left as air is blown outward.
Global Winds And Local Winds Ppt Video Online Download
Option A Explanation.
. These are called geostrophic wind s. Horizontal flow is called advection. Warm dry wind flowing from east side of Rockies.
Water vapor carbon dioxide and other gases absorb and reradiate thermal energy. This changes the general circulation pattern of the air. Because such a plane is in practise comprised of elements and joints the term air barrier system ABS is preferred.
When you stand with your back to the wind in the Northern Hemisphere low pressure is always to your left. Indian word meaning snow eater. With and without rain.
Pressure is high in the centre and decreases towards the outsideIII. Transfer of energy by circulation or movement of a gas. Air flowing from areas of high pressure to low pressure creates winds.
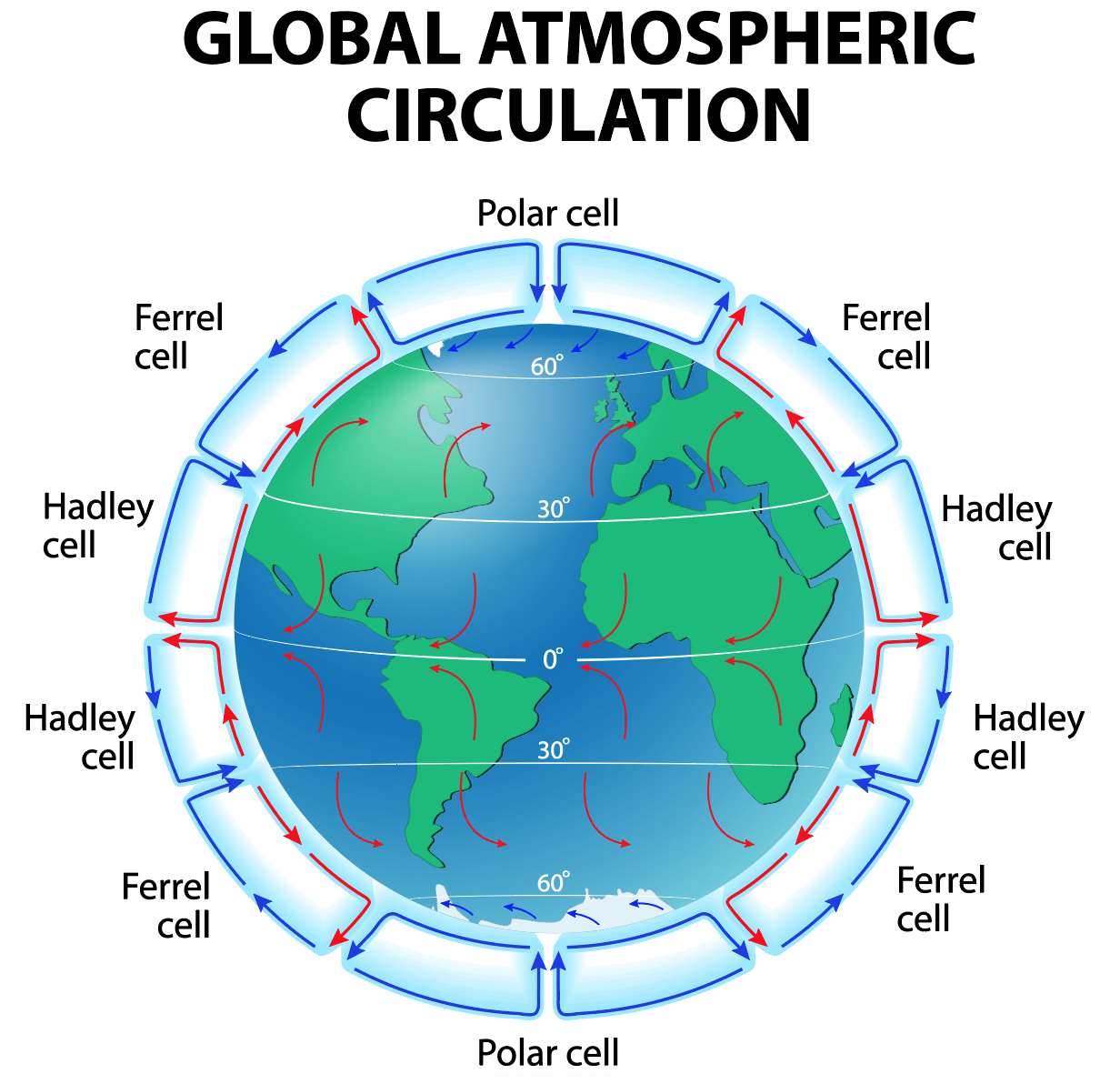
Depression in the southern hemisphere is a mass of air whose isobars form an oval or circular shape. In 1857 Dutch meteorologist Christoph Buys Ballot formulated a law about geostrophic winds. Bands of high pressure and low pressure founf every 30degrees of latitude.
A convection cell is most notable in the formation of clouds with its release and transportation of energy. Similar phenomena exist elsewhere in the world and have their own names Alps foehn Temperature may rise as much as 36 F 20 C in 1 hr plus sharp drop in RH Two kinds of chinook. This is called anticyclonic flow.
In the Southern Hemisphere they turn to the left. Coriolis effect is demonstrated using a metal ball and a rotating plate in this video. In the tropics near the equator warm air rises.
The Gulf Stream is the western boundary current of the gyre. The air cools until it descends. The movement of air through Earths -- or any planets -- atmosphere is called wind and the main cause of Earths winds is uneven heating by the sun.
When it gets about 10-15 km 6-9 miles above the Earth surface it starts to flow away from the equator and towards the poles. A pileus also called scarf cloud or cap cloud is a small horizontal altostratus cloud that can appear above a cumulus or cumulonimbus cloud giving the parent cloud a characteristic hoodlike appearance. Swirling in the opposite direction from a low pressure system the winds of a high pressure system rotate clockwise north of the equator and counterclockwise south of the equator.
The Coriolis force deflects air to the right in. The rising air at the equatorial regions and the sinking air at about 30N and 30S form huge convection current known as a Hadley cell for the English meteorologist who first proposed their existence to explain the trade winds. Cool air that moves down mountain slopes during the night is called.
Air masses These global wind patterns drive large bodies of air called air masses. Warm air that rises up mountain slopes during the day is called. Subsequently the air flows to the rear through the transition region called a turbulent flow region but the layer in contact with the flat plate surface is in the laminar flow state with a remarkably low flow rate.
The air moving back toward the equator forms warm steady winds known as the trade winds. The direction that they spin depends on the hemisphere that they are in. I and III D.
The hot air flows toward the poles and the cold air moves toward the equator. SINKING air causes HIGH PRESSure because. The name and description of the characteristics of large air masses present in the atmosphere.
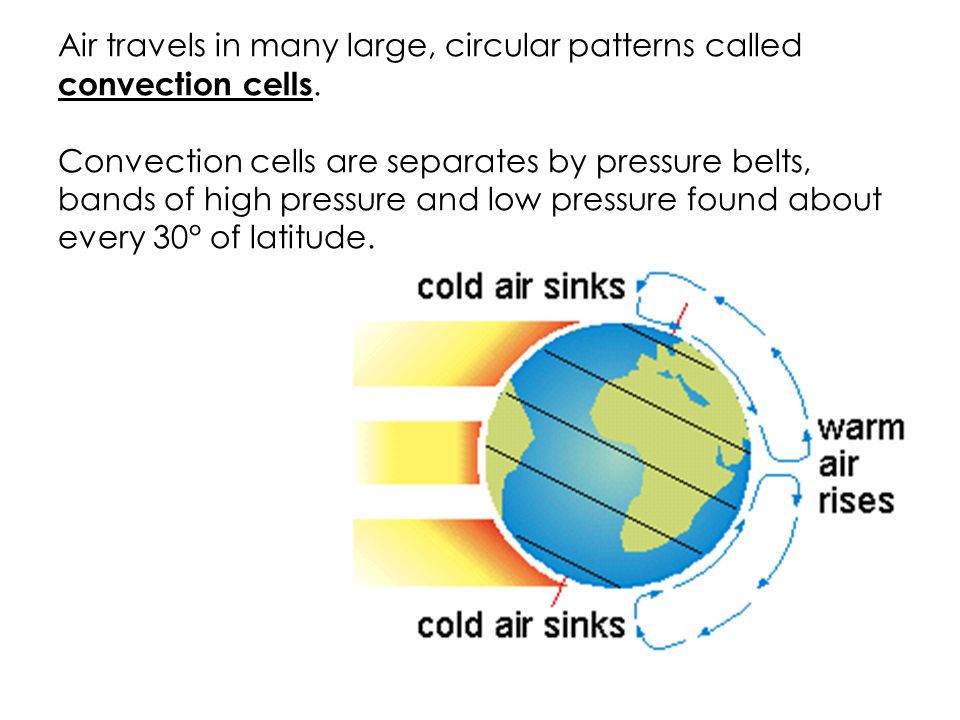
What are the large circular patterns air travels in called. This uneven heating causes changes of atmospheric pressure and winds blow from regions with high pressure to those with low. For example air over the tropical ocean becomes exceptionally hot and humid.
Air moves anti-clockwise A. The location over which an air mass forms will determine its characteristics. Air masses are thousands of feet thick and extend across large areas of the Earth.
Convection currents are defined as the vertical movement of heat or moisture energy from one location to another primarily due to the temperature changes within the substance. The vicinity of the leading edge is called the laminar flow area where air flows parallel to the flat surface. The primary plane of air flow control in a wall is generally called the air barrier.
Where it reaches the ground it creates a high pressure zone. Convection cells are seperated by. Still flowing in a circular pattern the current flows south as far as the northwestern coast of Africa where it is known as the Canary Currentthe gyres eastern boundary current.
Cool air that flows over the land toward the ocean during the night is called. It is a mass of air whose isobars form an oval or circular shapeII. Transfer of energy as electromagnetic waves.
Air travels in large CIRCULAR patterns called. Its also affected by the spin of the Earth. It significantly affects air that moves over great distances.
Circular movement of warm air rising and cool air sinking. The Coriolis effect causes winds and currents to form circular patterns. The winds would blow in straight lines but since the earth rotates they are turned at an angle.
The speed of the Earths rotation causes the general flow Figure 8 to. Air from the surrounding area is sucked into the space left by the rising air. This pattern called atmospheric circulation is caused because the Sun heats the Earth more at the equator than at the poles.
This bending of the winds is called the Coriolis effect. In the Northern Hemisphere they turn to the right. They are formed by strong updrafts acting upon moist air at lower altitudes causing the air to cool to its dew point.
Air flows horizontally at top of the troposphere. Some of the examples of convection current may include boiling water convection currents in the atmosphere and in the ocean weather changes campfires etc. The gyre then becomes the North Atlantic Current which flows across the North Atlantic to Europe.
Air moves in large circular patterns called convection cells. In the Southern Hemisphere low-pressure systems will be on your right Wind Zones.
What Is Global Atmospheric Circulation Internet Geography
Atmospheric Circulation Wikipedia

What Are The Narrow Belts Of Winds That Can Reach 250 Mph Called 0 Of Jet Currents 2 Convection Currents 3 Jet Streams 4 Convection Streams Ppt Download

A Global Look At Moving Air Atmospheric Circulation Center For Science Education

Wind The Movement Of Air By Differences In Air Pressure Air Moves From Areas Of High Pressure To Areas Of Low Pressure Air Moves In Small Circular Patterns Ppt Download

0 comments
Post a Comment